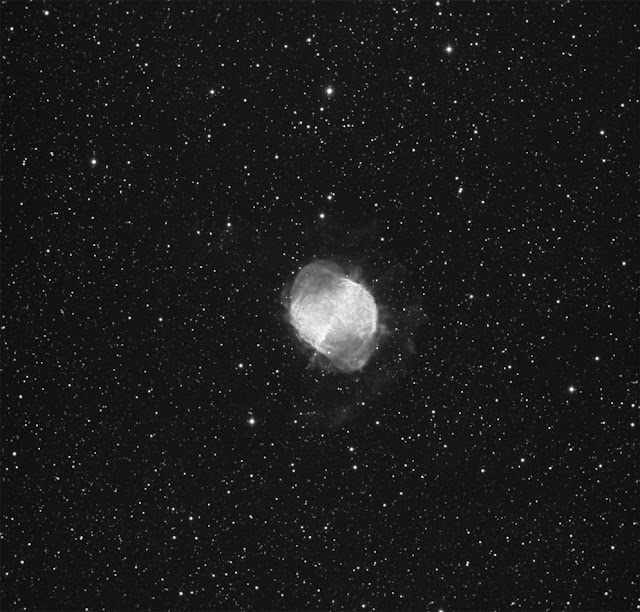
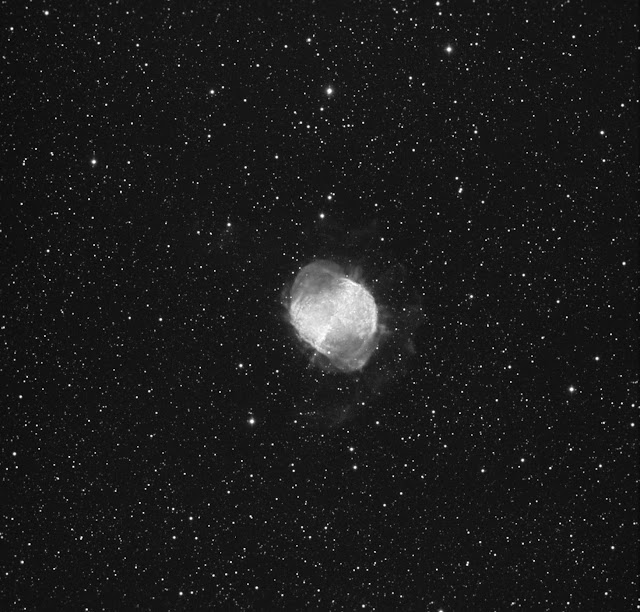
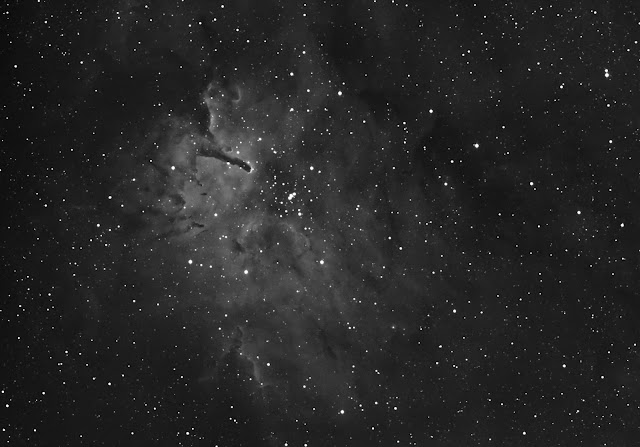
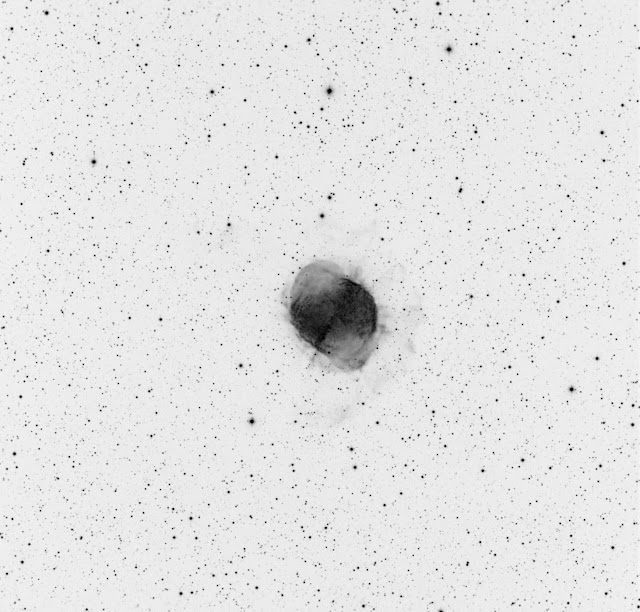
The Elephant's Trunk nebula is now thought to be a site of star formation, containing several very young (less than 100,000 yr) stars that were discovered in infrared images in 2003. Two older (but still young, a couple of million years, by the standards of stars, which live for billions of years) stars are present in a small, circular cavity in the head of the globule. Winds from these young stars may have emptied the cavity.
The combined action of the light from the massive star ionizing and compressing the rim of the cloud, and the wind from the young stars shifting gas from the center outward lead to very high compression in the Elephant's Trunk nebula. This pressure has triggered the current generation of protostars.[2]
Instruments and exposure data:
W.O FLT110 with dedicated TMB field flattener
FeatherTouch 3'' focuser
Starizona MicroTouch autofocuser
W.O ZS80 ED
SBIG ST10XME CFW9
Meade DSI
SBIG ST10XME CFW9
Meade DSI
Filters:
Ha 5nm Astrodon
Sky-Watcher EQ6 Pro
Ha :29*15min bin1x1














60.jpg)




GBcopy3-68%25.jpg)
GB.jpg)